Trying to better understand SEO? Struggling with all the terms? Then our back to basic guide is perfect for you.
Updated: Aug 26, 2020
We have created this guide as a complete beginners introduction to the world of SEO, it covers almost every topic we could think of to help you.
Ready to start driving more website traffic to your site using SEO? In this Beginner’s Guide To SEO, we’ll walk you through:
What is SEO?
Before we delve into the various SEO strategies that you can use, let’s take a second to address the question… what exactly is SEO?

In a nutshell, SEO refers to Search Engine Optimization, which is the process of ranking your website on search engines in order to generate organic traffic to your site.
Technically speaking, SEO deals with all the search engines in the market, including Bing, and Yahoo.
That said, since Google is by far the most popular search engine, people who say “I need to improve my website’s SEO” generally mean that they want to optimize their website specifically to rank on Google.
SEO can be categorized into various branches, including white hat vs black hat SEO, and on-page vs off-page SEO.
We’ll explain these in greater detail further on in this article!
Ranking Factors for Google
Here’s a question that we get a lot: what are the SEO ranking factors that affect my website’s visibility?
We’ve covered a lot of ground in the previous sections, so take a few seconds to internalize and digest all the information.
Once you’re done, we’ll move on to talking about how you can optimize your website to rank on Google!
- Keyword Research
- Quality Content
- Click through rate
- Bounce rate
- On-Page SEO
- SEO Friendly URLs
- Title tags
- Meta description
- Image SEO
- Internal linking
- Schema Markup
- Featured Snippets
- Backend Optimization
- Building backlinks
- Dofollow vs Nofollow
- How to build backlinks
Keyword Research
The first step of any SEO strategy is always keyword research.
Here, you’ll identify which keywords you should target in order to drive high quality traffic to your site.
There’s two ways I like to do this, one is using SEMrush to get ideas and the second is Googles own keyword planner.
SEMrush method
Google method
To get started, sign into your Google Ads account (or create an account if you haven’t already got one).
Next, click on “Tools” from the top panel, then on “Keyword Planner”.
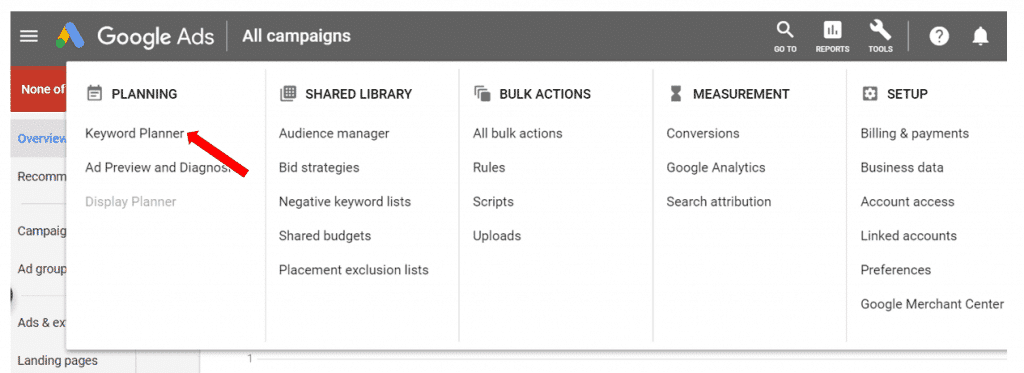
From here, click on “Find new keywords”, and enter words, phrases, or a URL related to your business.
If I’m running a marketing agency in Michigan, for example, I might key in “marketing agency Michigan”.
Google will then spit out a list of related keywords that might be interesting for me to target:
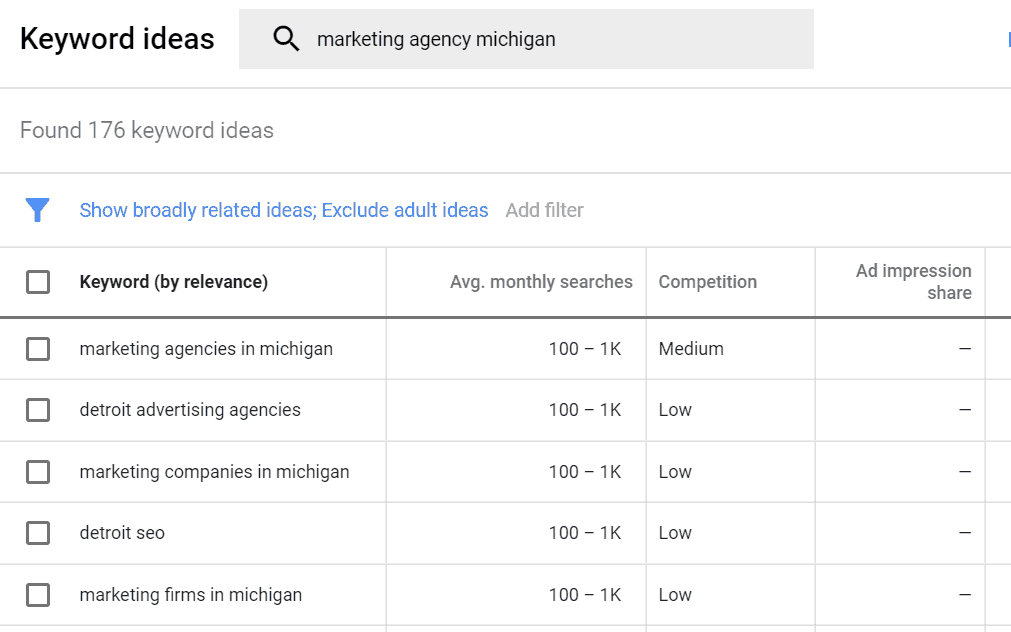
Ideally speaking, you’d want to target keywords which have high average monthly searches, and low competition.
These keywords have the potential to bring a ton of traffic to your site, but at the same time, aren’t too tough to rank for.
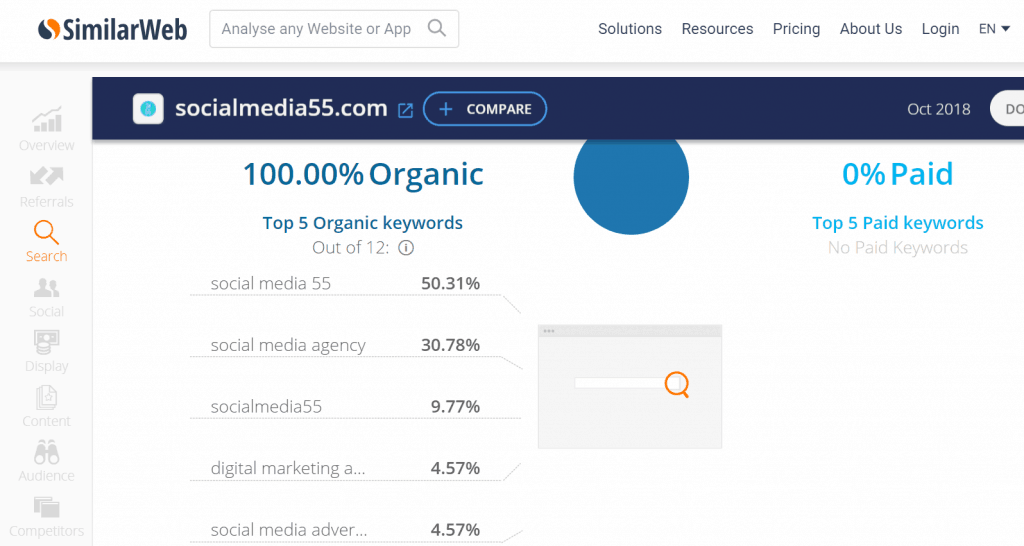
Once you’re done researching keyword ideas using Google’s Keyword Planner, hop over to SimilarWeb, and key in the URL of one of your competitors.
Using traffic checker sites such as similarweb or alexa are a great way to get a better insight on your competition.
For example, after searching for socialmedia55.com, I can see a list of their top 5 best-performing organic keywords:
Now, here’s the question:
should you take your competitors head-on, and try to rank for their keywords, or should you avoid the keywords they’re already ranking for, and target different keywords?
First up, if your competitor is ranking for their branded keywords (eg: socialmedia55’s top performing keyword is “social media 55”), you obviously wouldn’t want to target these keywords as well.
After all, if someone searches for your competitor’s brand keyword, they’re looking to learn more about your competitor.
Even if you try and distract them and draw them to your site, chances are that they’ll bounce quickly.
This indicates to Google that your content doesn’t match your site visitors’ search intent, and results in you being pushed down the search rankings.
The bottom line? You’ll find it hard to rank on the first few pages of Google if you’re targeting your competitors’ keywords, so this isn’t a good strategy.
(You can, however, bid on your competitors’ keywords when you buy traffic via PPC, but that’s a topic for another day!)

How about targeting the other keywords (non-branded ones!) that your competitor is currently ranking for?
To decide whether you want to do this, browse through your competitor’s website, and evaluate how they’re doing in terms of content.
If your competitor has been blogging since 2008, and they’re putting out amazing, high-quality content, then it might be pretty tough for you to catch up to and outrank your competitor.
Under these circumstances, targeting other keywords might be a better approach.
If your competitor isn’t doing particularly well in their content, however, and you think you can take them on, go ahead and target their keywords.
As long as you follow the tips we’ve outlined in this guide, you’ll have a decent chance of beating them at their own game!
Keyword research tools
Google’s Keywords Planner and SimilarWeb aside, other keyword research tools include:
- Moz’s Keyword Explorer
- SEMrush’s Keyword Difficulty Tool
- Google Trends
- Keyword Shitter
- AdWord & SEO Keyword Permutation Generator
- AnswerThePublic
- LSIGraph
- Wordtracker’s Scout
- Keywords Everywhere
Go ahead and knock yourself out!
Short tail vs long tail keywords
If you’re not sure what short tail and long tail keywords are, here’s a quick break down: short tail keywords are keywords consisting of three or less words, and long tail keywords are keywords consisting of longer phrases. Short tail keywords are also commonly referred to as “head” keywords.

In a nutshell: short tail keywords boast higher search volumes, but they lose out when it comes to conversions and competition.
Long tail keywords get less searches (individually!), but they’re easier to rank for and convert more effectively.
Let’s use the same example of a marketing agency in Michigan:
There might be a lot of people searching for a short tail keyword such as “marketing agency Michigan”, but chances are, you’ll find it hard to rank for such a competitive keyword.
Even if you DO manage to rank for this keyword, you’ll probably find it hard to convert the visitors that click through to your site, because your keyword is so broad.
Bearing this in mind, a better bet is to use a long tail keyword such as “SEO digital marketing agency in Detroit”.
First up, you’re narrowing it down when it comes to location, which helps shave off a lot of unqualified traffic.
On top of that, specifying that your marketing agency specializes in SEO and digital efforts also helps you generate website traffic that’s a better fit.
Last but not least, honing in on a more specific, niche term reduces the competition you’ll have to face.
This means you’ll rank more easily for your chosen keyword. It’s a win-win, whichever way you look at it!
Common keyword mistake: using “clickbait” keywords
Now, one common keyword mistake that plenty of business owners make is using “clickbait” keywords.
Let’s run with that same example of a marketing agency — this marketing agency might choose to target the keywords “content marketing hacks” or “free content marketing techniques”, thinking that these keywords might entice searchers, and bring them a ton of traffic.

Why is this a bad strategy? Well, first things first — if you produce a blog article titled 19 Amazing Content Marketing Hacks You Need To Try, and it turns out that these 19 “hacks” are actually just regular tips and not actual hacks, then your audience won’t react kindly to your content.
At the end of the day, no one likes being misled!
On top of that, creating content around keywords such as “hacks”, “free” and “cheap” will bring in visitors without purchasing power.
If these visitors have the budget to spend on engaging the services of a marketing agency, they probably wouldn’t be googling for “free content marketing techniques”.
Moral of the story? Choose your keywords wisely, and don’t give into the temptation of targeting “clickbait” keywords that aren’t actually a good fit for your company or brand.
Quality Content
The next part of the puzzle lies in creating high quality content. There are a few things to consider here, including:
- What you should include in your content
- The voice and tone of your content, and
- How you format your content.
First things first, when it comes to what you should include in your content.
Here’s a good rule of thumb: create a piece of content that’s 10x better than that of your competitors.
To do this, simply search for the keyword that you want to target, and check out all the existing results on the first page of Google.
Your content has to include ALL the material covered by these articles, and then some.
Next, make sure you nail the voice and tone of your content as well.
Assuming you’re creating long form content (>1000 words), you’ll want to utilize a conversational tone and keep things light-hearted and fun.
This way, you’ll engage your readers more effectively; the goal is to sustain their interest throughout the article.

As a general rule of thumb, try to use first and second person pronouns instead of writing in the third person.
Depending on your company’s brand, you might also be able to get away with using colloquial terms, GIFs and emojis in your content.
Last but not least, make sure you format your content in a way that’s easy to read.
Remember: the vast majority of people consume content on their mobile devices, NOT on their desktops and laptops.
You’ll want to break up your text with plenty of images, and not subject your readers to walls and walls of texts.
On top of that, also utilize bullet points, headers, and break your paragraphs up so that they don’t contain too many sentences.
If you want some inspiration, check out Backlinko’s blog.
Although they put out a ton of long-form content, their blog posts are always well-formatted and easy to read:
Other content factors to consider
As a marketer or a business owner, you don’t have much control over the searcher-related factors we’ve just discussed, but you can work on publisher-side factors to boost your visibility on Google.

Now, Matt Cutts from Google has publicly stated that there are over 200 variables in the Google algorithm, so there are a lot of moving parts that you’re dealing with here.
Obviously, you won’t be able to optimize your site around all 200 variables (Google doesn’t even disclose the complete list of variables!), but here are some of the key factors that you should look out for…
Quality of article
If your article is well-written, and it provides value to your readers, then this increases your chances of ranking on Google.
Bearing this in mind, you should be writing for your readers, NOT for search engines.
Don’t mindlessly stuff keywords into your article, thinking that this will get you into Google’s good books!
Click through rate
When you have a high click through rate, this tells Google that people find your search result relevant, and they want to consume your content.
Google will adjust their results accordingly, and rank you higher on their page.
How do you increase your click through rate?
First, make sure you’ve got a powerful, intriguing title that stands out from the other titles on the page. Also, include a Call To Action (CTA) in your meta description to encourage readers to click through.
Bounce rate
Your click through rate may be important, but it’s only one piece of the puzzle.
If you enjoy high click through rates on your listings, but your bounce rates are high as well, that’s an indication that your content doesn’t meet your reader’s needs — so it’s back to square one.

For those who aren’t 100% sure what your bounce rate is, this is basically the percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page.
Think about it: if someone navigates to your site via Google, and they find your site helpful, they’ll probably stick around and check out your additional pages (other than the one they landed on).
If you have plenty of visitors who are exiting directly from your home page, on the other hand, that’s a sign that your content isn’t as compelling or relevant as you think it is.
To Google, that’s a red flag. That’s why it’s important to keep your bounce rates as low as possible!
On-Page SEO
Now that you’ve crafted a kickass article, the next step is to cover all your bases when it comes to your on-page elements. These elements include:
- URLs
- Title tag
- H2 tags
- Meta descriptions
- Image file names, alt text and title tags
- Internal links
- Schema markup
Read on to find out more!
SEO Friendly URLs
First up, your URL should be short, sweet and to the point.
(In fact, Google’s Matt Cutts previously talked about how Google’s algorithm favors URLs with three to five words.)
Here’s a negative example: https://www.XYZmarketingagency.com/blog/archive/11/08/2018/7-marketing-best-practices-that-every-small-business-owner-should-follow
And a positive example:
https://www.XYZmarketingagency.com/marketing-best-practices
On top of that, be sure to get your keywords into your URL, and make sure that your URL is readable:
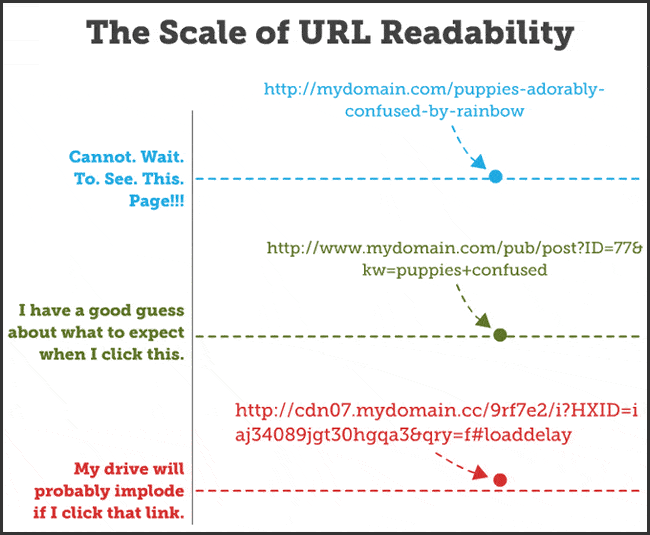
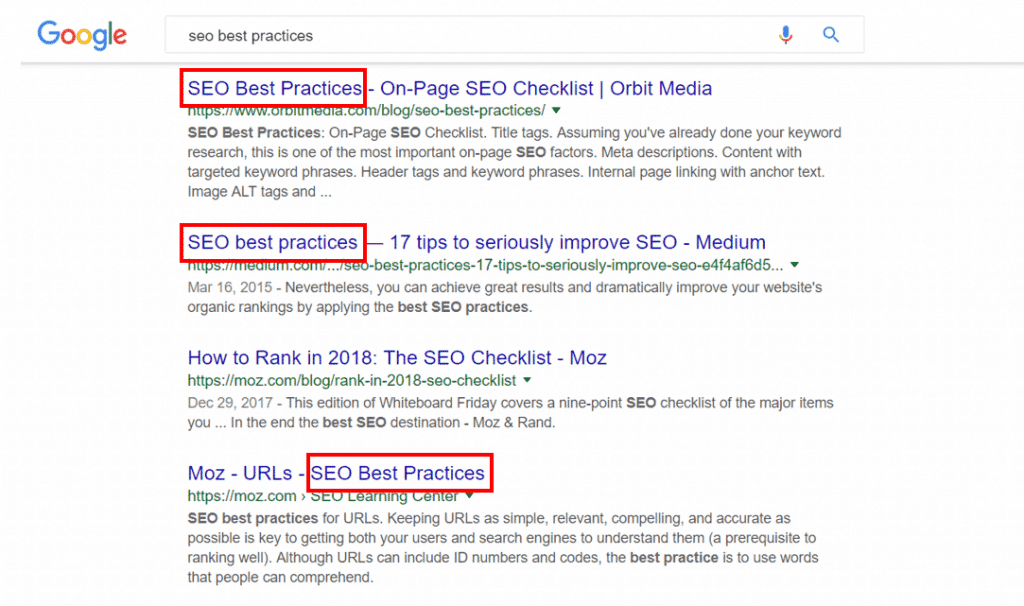
Next up, your title tag should also contain your keyword (at the front, if possible!), and be simple and easy to read.
Check it out: when I google the term “SEO best practices”, the top two organic results both feature title tags with the keyword loaded up front.
H2 Tags
Title tags aside, you also have your H2 tags, which you’ll use to structure your article.
The same goes for these tags — you’ll want to incorporate your keywords in them as much as possible (in a natural way, though).
Meta description
Then there are your meta descriptions, which are the snippets of text that Google displays on your search listing, right below your title tag.
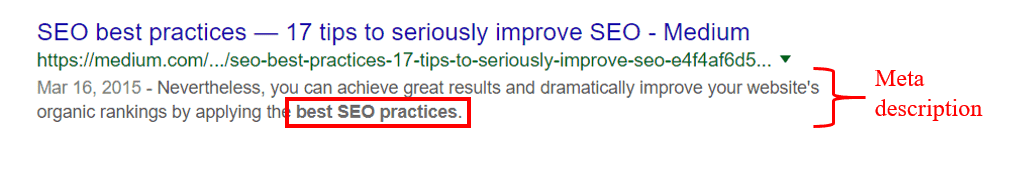
Again, you’ll want to incorporate your keywords into your meta description.
Google actually bolds these keywords, and this helps your search result stand out to searchers.
All things being equal, you’ll enjoy higher click through rates on your listing, which will in turn increase your Google ranking!
Image SEO
Alright, moving on to your images. There are various things to get right here, including your image file names, alt text and descriptions.
First and foremost, make sure you rename your file name to something that’s relevant.
As always: use your keywords if possible.
Negative example: DSC2008.jpg
Positive example: marketing-agency-SEO-case-study.jpg
On top of that, you’ll want to input your alt text and descriptions, and utilize your keywords in those as well.
Here’s a quick breakdown of exactly what these are: alt text, also known as alternative text, is essentially a field used to display text that describes an image to “alternative” sources (these include blind individuals who use screen readers).
Image title text, on the other hand, is simply an attribute that’s used to provide additional information for an image.
There’s no hard and fast rule when it comes to how you should word your alt text and image title tags, apart from the obvious: use your keywords without spamming them.
If you have a screenshot of your Google Ads dashboard on your article titled How To Set Up Your Very First Google Ads Campaign, for example, you might use “google ads dashboard” as your alt text and “how to create google ads” as your title tag.
Internal linking
The next item you’ll want to optimize are your internal links. All you have to do here is to add 2-3 internal links on your page!

Doing this helps your readers discover related content, and it also helps search engines crawl your website more effectively.
Be sure to make sure that your links are included in a natural way; don’t force it. Also, try and use descriptive instead of generic link text.
Positive example: Read our guide on How To Set Up Your Very First Google Ads Campaign to find out more.
Negative example: Click here to read our guide on How To Set Up Your Very First Google Ads Campaign.
Schema Markup
What exactly is Schema markup?
It’s a set of code or microdata that’s added to your HTML in order to help search engines read your page and rank it more effectively.
Once you add Schema markup to your HTML, this allows you to display rich snippets below your page title, and this in turn draws more searchers to click on your listing.
In case you still can’t wrap your head around Schema markup, here’s a real-life example:
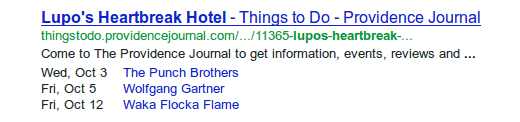
See how there’s a schedule of upcoming events displayed under this hotel’s listing? That’s done using Schema markup!
For marketers and business owners, utilizing Schema markup is a great way to engage searchers, and gain a leg up on your competition.
According to statistics, only 0.3% of all websites use schema markup. So start adding Schema markup to your HTML, and have your search results stand out!
To learn how to add Schema markup to your HTML, check out Neil Patel’s guide.
Featured Snippets
In a recent blog post, Google defines a Featured Snippet as a “descriptive box at the top of Google’s results”.
More specifically, Google goes on to say:
“We display featured snippets in search when we believe this format will help people more easily discover what they’re seeking, both from the description and when they click on the link to read the page itself.
It’s especially helpful for those on mobile or searching by voice.”
Here’s an example: say you have a Google Home in front of you, and you ask: “Okay, Google, tell me why is the sky blue?”
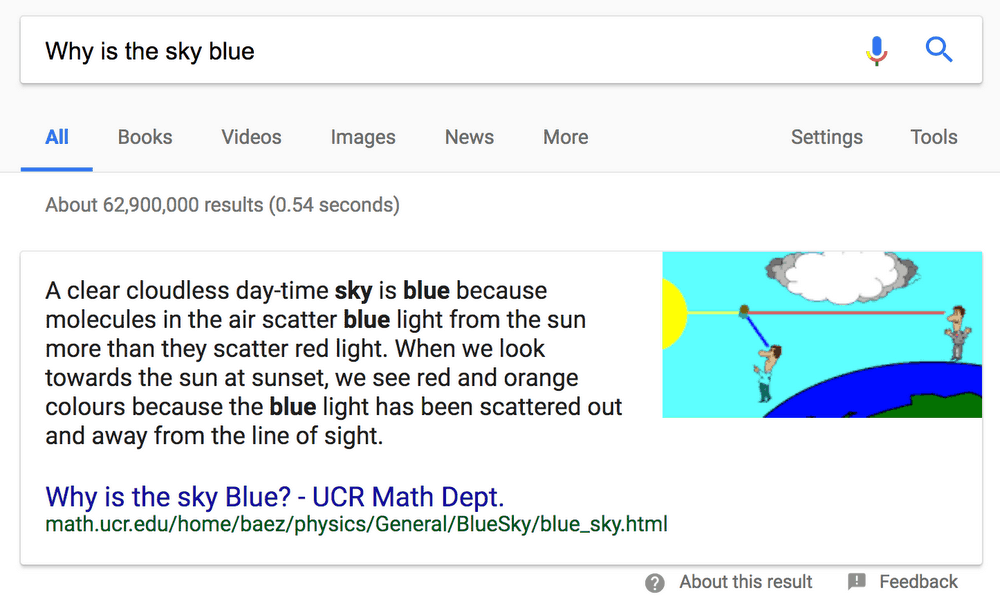
Your Google Home will reply: “According to UCR, a clear cloudless day-time sky is blue because molecules in the air scatter blue light from the sun more than they scatter red light.”
As you can see, voice search requires on a highly conversational talking style, with search queries being framed in simple questions.
If you break down these questions according to their question type, you’ll also find that the bulk of the questions are “how to” or “what” type questions.
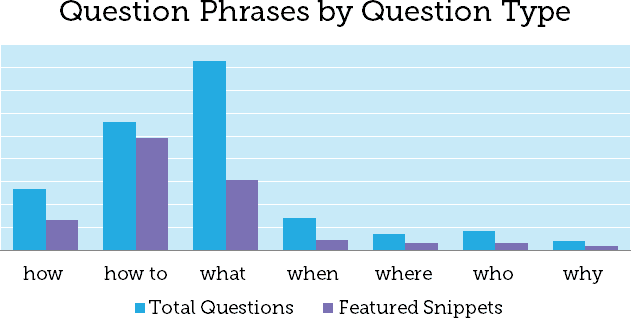
With this nugget of information, you can easily optimize your content to be more relevant to your consumers’ search queries.
If you own an eCommerce store selling leather goods, and you want to create content about taking care of leather bags, for example, it makes more sense for you to optimize your article around a long-tail keyword such as “How to clean and maintain leather bags”.
Backend Optimization
Cool beans, you’ve now got all your on-page elements optimized and good to go.
It’s time to move on to the next step… optimizing the backend of your site!
Information Architecture: How to organize your website
Information architecture sounds like a pretty fancy term, but it simply refers to how you organize and lay out the pages on your website.
What does this have to do with SEO? Well, the way that you organize your website and link the various pages of your website affects the SEO of your individual pages.
More specifically, if you link to Page A multiple times from different pages within your site.
This tells Google that this page contains important content, and it increases the chances that Google will rank it highly.

Now, let’s tie this into your overarching SEO and content strategy…
As discussed earlier, you’ll be producing plenty of informative, high quality content in the hopes that these will rank on Google.
Assuming that you hit a homerun with one of your articles, and this article generates a ton of traffic plus backlinks (from external websites!), you’ll now want to milk this article and link from it to your other pages.
How does this work?
Well, because this specific article is so well-received, it carries a ton of “SEO juice”, and it’s highly regarded by Google.
In order to maximize your mileage from this article, you’ll want to link from this article to your other pages (say, your /pricing or /free-trial page) that you’re hoping will rank as well.
This way, you’ll pass some of this article’s authority to these other pages.
On top of linking from your well-performing content to your other pages, another best practice includes structuring the content within your site using a “flat” hierarchy.
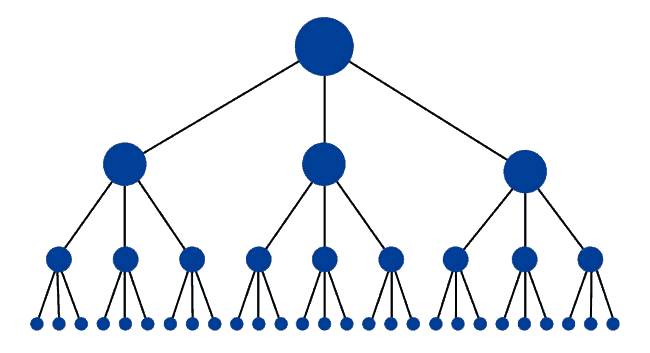
In layman terms, this means making the pages on your website easy to navigate to, and not concealing any pages deep within your website.
Ideally, your visitors should be able to reach all the pages within a few clicks of your home page and/or your most linked-to pages.
Other technical factors to take into consideration
Information architecture aside, there are other factors to take into consideration when optimizing the backend of your site.
As a general rule of thumb, you site should be easy to crawl, mobile-friendly, and HTTPS/SSL secure. It should also load quickly on your visitors’ devices.
First up, to make your website easier to crawl, make sure you’ve got plenty of internal links that tell Google’s bots how each website page relates to its counterparts.
On top of that, you can also create an XML sitemap; this consists of a complete list of URLs on your website, plus information about when each URL was last updated, and how often each URL gets updated.
Assuming you’re using WordPress to power your site, creating an XML sitemap is easy.
There are plenty of plugins (see: Google XML Sitemaps) that will help you do the trick.
Next up, make sure that your website is mobile-friendly and mobile-optimized as well.
Google started moving to mobile-first indexing back in 2016, which means that it’s now using the mobile version of a site’s content (not the desktop version!) to rank pages from that site. Obviously, if your content isn’t mobile-friendly and optimized, you’ll lose out.
How do you tell if your website is mobile-friendly? Simple — use Google’s Mobile Friendly Test tool to find out.
If you need additional tips on optimizing your website for mobile, check out Google’s guide to mobile optimization.
Other than being mobile-friendly, your website should also be quick to load.
This might not be a factor that directly impacts your SEO, but it does cause a trickle-down effect.
Consider this: the longer your website takes to load, the more visitors will get frustrated and bounce from your page.
Google takes page bounces into consideration when ranking websites (we’ve mentioned this before!), so this will definitely affect your chances of nabbing a spot on the first page of Google.
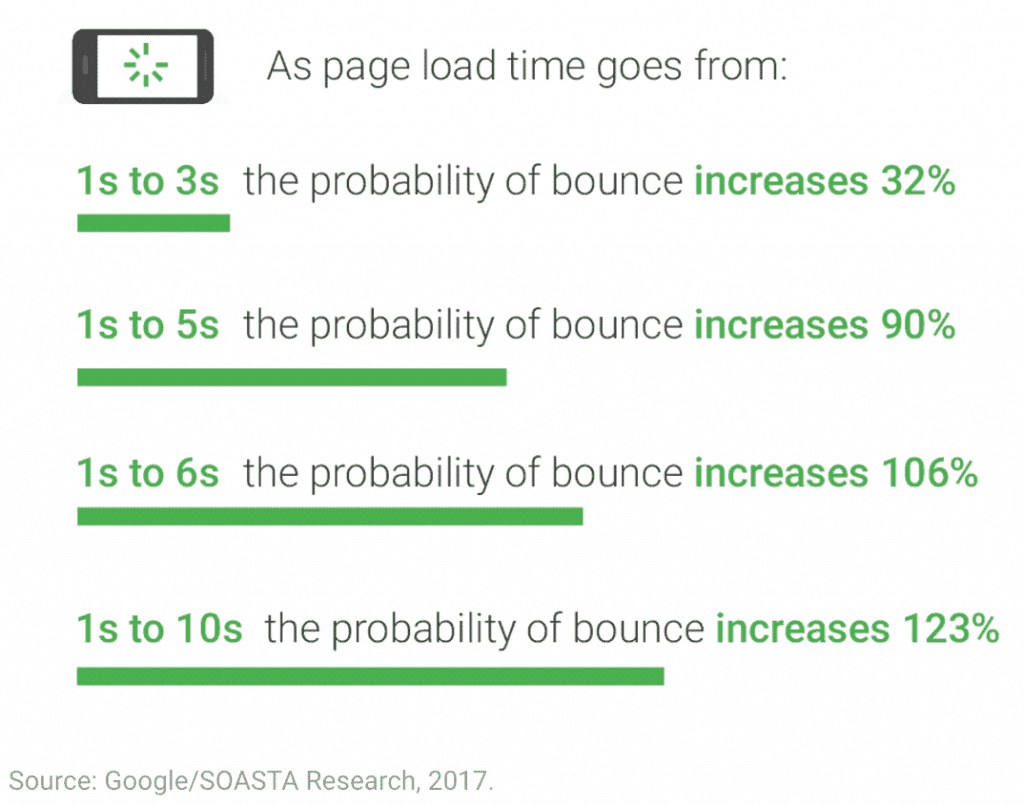
To assess your current page load speed, use Google’s Test My Site tool.
This tool will tell you how you’re faring when it comes to your page load speed, and it’ll also provide recommendations on how you can improve.
Last but not least, Google has outrightly said that HTTPS is a ranking signal, so you’ll want to ensure that your site is HTTPS/SSL secure.
To do this, you’ll have to purchase a security certificate from your domain registrar or another source, then set it up.
Where set up is concerned, we find that using a WordPress plugin (such as Really Simple SSL) is the easiest option.
Building backlinks
Simply put, backlinks are links from other websites to your websites.
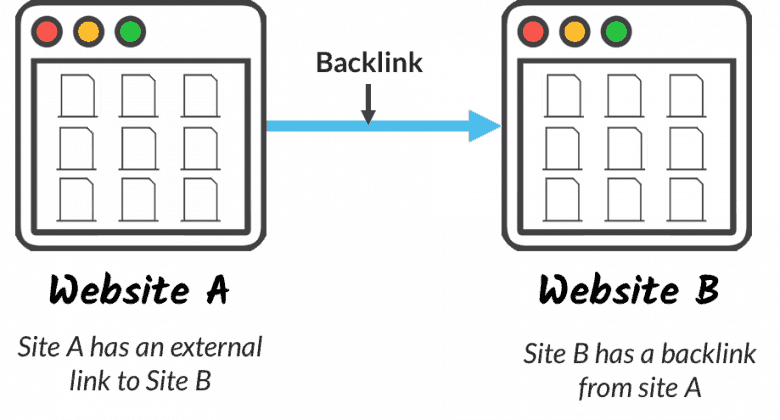
When it comes to backlinks, both quality and quantity are important. Ideally, you’d want to get as many backlinks as possible from high-quality, high Domain Authority sites. (For the uninitiated, high DA sites are reputable, high-ranking sites such as Forbes.com and Inc.com.)
Dofollow vs Nofollow
Backlinks can be categorized into dofollow and nofollow links.
Only the former (dofollow links!) pointing to your site will contribute to your site’s SEO; nofollow links do not help you build SEO juice in any way.

Now, let’s get into the nuts and bolts of what differentiates a dofollow link from a nofollow link. Basically, this boils down to the way a link is coded in HTML.
A standard dofollow link will look something along these lines:
<a href=”https://www.traffic-masters.net”>Traffic Masters
But a nofollow link, on the other hand, looks like this: <a rel=”nofollow” href=”https://www.traffic-masters.net”>Traffic Masters
Say you offer to guest-blog on a website (more on this later!) and they say they’d love to have you, BUT they can only give you a nofollow link, not a dofollow link.
Yes, this link still points back to your website, but it doesn’t help with your SEO rankings whatsoever.
How to build backlinks
If you’re already producing amazing, 10x content, then that’s half the battle won.
Given that your content provides a ton of value for readers, you should have plenty of folks who are willing to link to you in their articles.
That said, you’ll still have to work out a proper backlink strategy, and actively build your backlinks. Some people will reach out to influencers, and ask if they’d like to share their content:
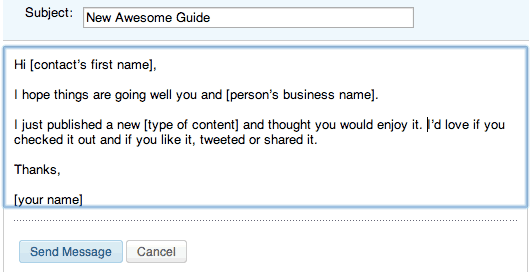
This works especially well if you’ve featured said influencer in your content (you might’ve quoted them, or referenced their case study, or anything along those lines).
On top of that, you can also actively seek out guest posting opportunities.
Just make sure that the publication is of high quality, deals with the same industry that you do, and gives you dofollow links!
If you want to take this approach, check out: 150+ Sites to Guest Post in 2018.
Track key metrics and refine content
Your final step is to track your key metrics, and refine and optimize your content accordingly. Remember: there’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to SEO, and while you can follow certain best practices to start off with, you’ll still have to tailor and adopt your strategies to suit your business and consumers.
Here’s a list of SEO key metrics and other factors that you should monitor:
- Organic traffic
- Bounce rate
- Conversion rate
- Click through rate (available on Google Search Console)
- Pages indexed (available on Google Search Console)
- Pages crawled per day (available on Google Search Console)
- Crawl errors (available on Google Search Console)
- Exit pages (the pages that appear on the top of the list are the ones where most of your visitors are exiting your site from, so you’ll want to improve and optimize them!)
- Keywords that you’re ranking for
Searcher-related factors
Say you’ve logged on to Google to conduct a search.
Obviously, your search query will play a determining role in influencing your search results.
Apart from that, Google also takes your location, social network, and the device you use to conduct your search into consideration.

Location
This one’s fairly straightforward. Say you’re currently based in Paris, France, for example.
If you search “Restaurants in Paris”, Google will take it that you’re looking for restaurants in your city, and not restaurants in Paris, Texas.
Social network
On top of that, Google is also more likely to show you results that your friends and family have engaged with as well.
Say, for example, you search for “SEO tips 2018”, and Google has a choice of showing you Article A or Article B as the first result.
Assuming Google sees that one of your Google+ contacts has shared a link to Article B on their profile, then Google will bump this article that your acquaintance has shared to the top of your results page.
Device
Finally, Google also factors in the device you use to conduct your search when deciding what search results to serve to you.
If you’re browsing on a tablet or a phone, for example, Google will prioritize mobile-friendly and mobile-optimized content over other content.
Why is SEO important?
The answer to this question is fairly straightforward — SEO is important because it helps you generate more website traffic, and get more eyeballs on your brand.
All things being equal, this results in more leads, conversions, and revenue for you.
This begs the question: if you’re already getting plenty of traffic (from using a platform like ours to buy website traffic or organic means), then is it still important to invest time and money into SEO? The answer is a resounding yes.
If you’re already generating organic traffic…
Say you haven’t come up with a specific strategy to optimize your website to rank on Google, but you’re still getting a ton of organic traffic.
That’s a great start, but this doesn’t mean that you should just rest on your laurels and not work on your SEO strategy.

Why is this the case? Well, you might be getting plenty of organic traffic already, but there’s a high chance that said traffic isn’t high quality.
You’re probably ranking for a random assortment of keywords, some less effective than others, and this means that the visitors that you bring to your website using these keywords aren’t as easy to convert as they could be.
If you do have a well-rounded SEO strategy in place, on the other hand, you’ll have a few high-intent keywords that you’re optimizing your site for.
Because you’ve specifically chosen to optimize your site for these high-intent keywords, you’ll find it easier to convert your site visitors (generated using those keywords) into paying customers.
If you’re already generating paid traffic…
Alright, what if you’re already generating high quality, high-intent traffic to your site using PPC?
When you buy traffic online and run paid campaigns it’s a great way of getting more conversions and sales in the short-run, however are they sustainable in the long run?
Consider this: back in 2006, the average Cost Per Conversion on Google AdWords was just $7.63.
Fast forward to 2011, and this Cost Per Conversion jumped to $19.74.
In 2016, that Cost Per Conversion increased yet again, this time to $33.
Here’s the unfortunate truth: as more business owners start advertising on Google AdWords, this drives the cost of your campaigns up, and you’ll have to keep increasing your ad budget just to get the same results.

Of course, you can jump ship to another ad platform and buy social traffic from such as Facebook ads, but as long as the platform you’re on operate on a bidding model (where you bid for keywords, impressions, or ad clicks), the same thing will happen.
As more advertisers join the fray, you’ll find your ad campaigns becoming prohibitively expensive, and your margins getting thinner.
Now, don’t get us wrong — we’re not villainizing PPC, or saying that you should ditch all your paid marketing efforts.
PPC is an important part of marketing strategy, but you shouldn’t be overly reliant on it, and neglect organic strategies such as SEO.
So, here’s the bottom line…
If you’re already generating website traffic via your PPC campaigns, it’s still important to work on your SEO — this way, your traffic won’t come to a complete standstill in the event that your paid campaigns get too expensive.
And if you’re already generating organic traffic, that’s a step in the right direction — your next step should be to fine-tune your traffic, and make sure you’re ranking for the keywords that will bring you the most sales.
On-page vs off-page SEO
SEO can be categorized into on-page and off-page SEO.
You can think of on-page SEO as SEO efforts that occur within your website (and on your webpages), and off-page SEO as SEO efforts that occur outside your website.

On-page SEO basically deals with optimizing your website for search engines.
This includes:
- Optimizing on-page elements (page title, meta description, etc)
- Structuring and organizing your website properly
- Optimizing your website load speed
- Linking articles and web pages internally
Off-page SEO, on the other hand, is all about promoting your website via external sources.
Off-page SEO strategies include:
- Building links
- Promoting content on social media
We’ve mentioned previously that it’s important to create a well-rounded SEO strategy — and that entails focusing on both on-page and off-page SEO.
Think of on-page SEO as your “foundation” — you’ve got to have high quality, well-structured content in order to rank on Google.
Once you’ve nailed your on-page elements, you’ll also want to use off-page strategies to distribute your content and allow it to reach a wider audience. On-page and off-page go hand in hand!
White hat vs black hat SEO
If you check out SEO forums online, you might see people discussing “white hat” versus “black hat” techniques.
With white hat SEO, the objective is to put out high quality, amazing content (which is what we’ve been discussing).
Black hat SEO, on the other hand, deals with using unsanctioned shortcuts and hacks to game the system.
More specifically, black hat techniques include:
- Posting duplicate content
- Using invisible text and stuffing keywords
- Cloaking or re-directing (for example: inserting text or keywords into a page only when the user performing the request is a search engine, not a human visitor)
Now, Google states clearly and unambiguously in its Webmaster Guidelines that these black hat techniques aren’t allowed.
To make sure you aren’t accidentally flouting Google’s guidelines, check out the entire list of techniques that they disallow:
- Automatically generated content
- Participating in link schemes
- Creating pages with little or no original content
- Cloaking
- Sneaky redirects
- Hidden text or links
- Doorway pages
- Scraped content
- Participating in affiliate programs without adding sufficient value
- Loading pages with irrelevant keywords
- Creating pages with malicious behavior, such as phishing or installing viruses, trojans, or other badware
- Abusing rich snippets markup
- Sending automated queries to Google
If you’re on the fence about whether you should use a particular technique or not, Google has a great sniff test that you can use.
All you need to do is ask: “Does this help my users? Would I do this if search engines didn’t exist?”
What happens if you use black hat SEO?
Google is constantly updating their algorithm and crawlers to clamp down on marketers and business owners utilizing black hat tactics.
If you do engage in black hat SEO, there’s a high chance that you’ll get slapped with a Google Penalty.

What’s a Google Penalty? This is basically any sort of negative impact to your search rankings, brought about either by an algorithm update, or a manual review.
In this section, we’ll walk you through the three types of Google Penalties, and discuss how each one might affect your website traffic.
Automated rank demotions
If you wake up one day and realize that your website is suddenly generating much less traffic than it previously used to, then you’ve probably received a rank demotion.
Assuming you don’t get any emails notifying you about this, it’s likely that your website has been flagged out by Google’s latest algorithm which screens for black hat techniques.
How do you remedy this? You’ll have to read up on what algorithm changes Google has recently rolled out, and fix your site accordingly.
Manual rank demotions
Automated rank demotions aside, there’s also the possibility that your website (which has been optimized using black hat tactics!) could be hit with a manual rank demotion.
How do these work? Google has a team of employees who are tasked to manually de-rank websites whom they believe are trying to game the system.
You’ll know that this is a manual rank demotion, not an automated one, if you receive a notification telling you that your website’s been deranked.
Google will also give you tips on how to reverse this demotion, so simply follow the to-dos they’ve outlined, and you should get your original ranking reinstated.
Outright bans
These aren’t as common as automated and manual rank demotions, but there are cases in which Google will completely delist and ban your site.
Generally speaking, these bans are reserved for websites which blatantly abuse Google’s system.
Here’s an example: back in 2006, Google realized that BMW was using doorway pages stuffed with keywords to direct users to their German website bmw.de.
When searchers clicked on these listings via Google, they didn’t get redirected to a product page — instead, they were brought to a doorway page which contained a wall of keywords and nothing else.

These doorway pages do link to product pages (or whichever pages the searcher is hoping to get to), but they add an unnecessary step to the process.
This negatively impact a searcher’s online experience (which Google doesn’t want, of course).
Once Google found out that BMW was utilizing doorway pages to rank for keywords, it completely remove the company’s website from their index.
BMW promptly removed their doorway pages, and they were re-included in Google’s index after that.
Voice search SEO strategy
How has SEO evolved in the past five years?
Well, with voice assistants and smart speakers becoming more mainstream, consumers are increasingly choosing to conduct voice searches instead of traditional keyboard searches.
Here’s what we know: as of January 2018, there were an estimated one billion voice searches per month.
By 2019, the voice recognition market will be worth a cool $601 million.
And by 2020, 50% of all searches will be voice searches.
How do you incorporate voice search into your SEO strategy?
Google uses its Featured Snippets to drive voice search, so in order to have your content be read out by a voice assistant when someone conducts a voice search, you’ll first have to get Google to highlight your content on its Featured Snippets.
Common SEO Mistakes
Now that we’ve walked you through the step-by-step process of how to optimize your site to rank on Google, let’s take a look at some of the common SEO mistakes that marketers and business owners make.
Turn around time
Here’s what we’ve noticed: many marketers and business owners go into the SEO game with all their guns blazing, and they devote all their time and energy to optimizing their website to rank on Google.
But when they don’t see any results a week, two weeks, or a month down the road, they quickly become discouraged, and the time that they spend on SEO slowly grinds to a halt.
Yes, it can be discouraging to not see any results right off the bat, but SEO is a long-term strategy, and it’s unrealistic to expect your website to magically appear on page one of Google after a single month.
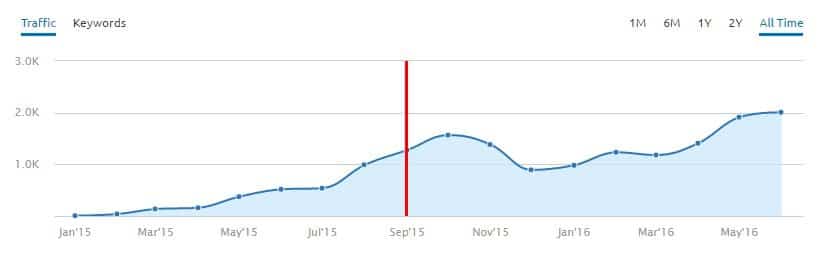
Generally speaking, it takes websites at least 6 months or longer to produce any meaningful results when it comes to SEO.
And that’s assuming you’ve covered all your bases, including both on-page and off-page.
If you’re choosing to focus on one particular arena first, you might take even longer to rank.
The same goes if all your competitors are way ahead of you when it comes to content marketing and SEO, or if you’re targeting highly competitive keywords.
User Intent
Another common SEO mistake that plenty of marketers and business owners make is neglecting user intent.
Remember: the key to producing a high-quality article that provides a ton of value to your readers is in identifying what your readers’ user intent, and matching your content to that intent.
For example, say you own a furniture eCommerce store, and you want to target the keyword “furniture maintenance tips”.
Now, you might come up with a couple of blog title ideas, including:
- Furniture Maintenance Tips: X Best Ways To Clean & Maintain Your Furniture
- Guide To Buying Furniture Online (+ 5 Furniture Maintenance Tips)
At first glance, both of the above titles look like good options, but once you delve deeper, you’ll realize that the first title is more relevant to your users, and matches their intent better.
If you go ahead with the second title, for example, you might devote the bulk of your article to talking about how to get a good deal on furniture online, plugging your store whilst you’re at it.
Obviously, this entire portion won’t be relevant to your reader, who’s specifically looking for furniture maintenance tips.
To get an idea of exactly how important user intent is, check out this guide by Backlinko.
In the article, Brian of Backlinko talks about how an article of his (which originally ranked on the first page of Google, and was a massive success) slowly decreased in ranking.
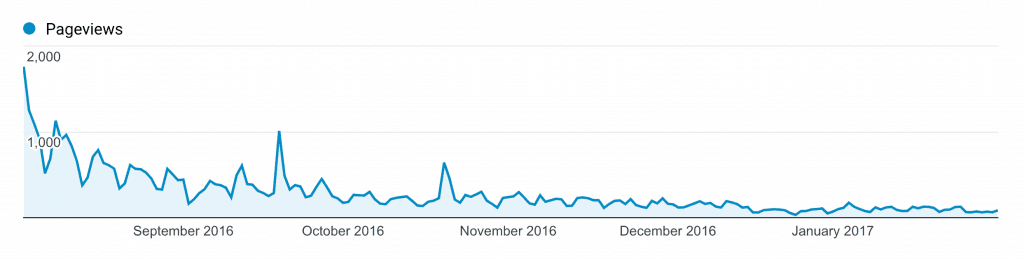
At the height of its traffic, this page got almost 2000+ sessions in a single day, but its traffic quickly tapered off, to the point where the page was only generating four to five page views per day.
This is DESPITE the fact that the page had 200+ backlinks, and plenty of comments and social shares.
After sitting down and doing some troubleshooting, Brian realized what the problem was — his page didn’t match his readers’ user intent.
He had optimized his page around the keyword “SEO checklist”, but his post was formatted to look like a case study, and not a traditional checklist.

After clicking on his listing, and getting redirected to his page, his readers realized that this wasn’t what they were looking for after all, and they’d exit his page and go back to Google.
This indicated to Google that Brian’s page wasn’t a good fit for this particular keyword, and his rankings dropped over time.
Now that Brian knew what the problem was, fixing it was fairly easy. He restructured and reframed his content, and edited the title of his post to reflect his readers’ user intent better:

Once he did that, his organic traffic shot back up, and his article was reinstated on Google’s first page.
Scraping content
Most marketers and business owners don’t actively set out to plagiarize or scrape content off other sites… but they end up doing it anyway.
Say you’re writing about how to take care of leather sofas, and you Google the topic just to find out what other people are saying.
You’re looking at a competitor’s blog post, and you come across a paragraph that’s nicely phrased:
You should, under no circumstances, let your leather sofa sit in direct sunlight.
If your leather sofa is exposed to intense heat or sunlight, discoloration will occur. Leather sofas can deteriorate quickly if they’re in a dusty environment, so be sure to wipe down your sofa regularly with a soft, smooth cloth.
You decide to take this content as your reference, and you paraphrase it to:
You should not let your leather sofa sit in direct sunlight. If your leather sofa is exposed to intense heat or sunlight, this will cause it to discolor.
Leather sofas can deteriorate quickly if they’re in a dusty place, so wipe down your sofa regularly with a cloth that’s soft and smooth.
Does that count as plagiarism? You’re basically just copying wholesale, and switching out a few phrases, so yes, it does.
In fact, according to Google’s guidelines, all of the following acts count as content scraping:
- Copying and republishing content from other sites without adding original content/value
- Copying content from other sites and modifying it slightly
- Reproducing content feeds from other sites without providing some type of unique organization or benefit to the reader
- Embedding content such as video, images, or other media from other sites without adding substantial value to the reader
Earlier in our White Hat vs Black Hat SEO section, we mentioned that “scraped content” was included in the list of tactics that Google considers black hat.
Bearing this in mind, stop “referencing” content from other websites, and come up with your own original, unique content!
Non-evergreen content
Many marketers and business owners like to produce “timely” content that coincides with the latest industry trends or updates.
Used properly, this can be a pretty smart move — you can use this strategy to increase your credibility, and be seen as a thought leader in your industry.

That said, you shouldn’t solely focus on covering industry updates, and ignore other more evergreen content.
“Industry update” type articles tend to have a pretty short shelf life, and they won’t be able to generate long-term traffic like how evergreen content does.
Take these two blog articles, for example.
- All You Need To Know About Google’s Latest Penguin Update.
- 10 Tried And Tested SEO Tips Straight From Google’s Own SEO Team
The first article might have gotten plenty of hits back when Google first pushed out its Penguin update, but it probably doesn’t generate any meaningful traffic now.
The second article, on the other hand, can generate a steady stream of website traffic for a publisher or business owner across many years.
Site Audits
The final mistake that many marketers and business owners make when it comes to SEO is… not auditing their websites regularly.
When you first embark on your SEO project, you’ll probably do a complete audit and overhaul of your website, and fix all the pesky technical problems.
That said, assuming you regularly update your site and install and use new plugins, you’ll want to conduct a periodic audit of your site, and ensure that you don’t have any new issues popping up.

For example, you might’ve removed your duplicate content previously, but these might crop up again due to pagination problems.
If you’ve recently reworked your categories or tags, or reworked your site organization, you might also have new broken links which you’ll have to fix.
So carve out an hour or two once a month, and sit down and conduct an SEO audit for your site. You don’t need to do this audit manually; simply make use of a free online tool such as SEOptimer.
BONUS: SEO case studies for inspiration
Want to learn more tried-and-tested SEO techniques from marketers who have been there, done that? Check out the following SEO case studies:
- SEO case study: Zero to 100,000 visitors in 12 months
- SEO Case Study: 11,065% More Organic Traffic in 6 Months
- From Zero to 50,000 Visitors in One Month
- Zero to One Million: an SEO Campaign Blueprint
- Case Study: How I Used a Case Study to Grow My Sales by 185%
Conclusion
Phew, you’ve made it to the end of this bumper guide on SEO, and you’re now an unofficial expert on all things SEO related.
Give yourself a pat on the back!
Now, we’re not going to lie — there are plenty of moving parts when it comes to SEO, and getting started with SEO can be intimidating to someone who’s a complete beginner or novice.
That said, everyone starts somewhere. Those sites who get upwards of 20,000 or 50,000 views every day?
They had to start from scratch too, and build their audience up slowly!
So stop twiddling your thumbs, and start your SEO journey today.
We’re not asking you to accomplish everything we’ve listed in this guide right off the bat — all you need to do for now is to look at our checklist of things to do and give yourself deadlines for each step.
(And perhaps get started researching your keywords, if you’re up to it!)
If you’re facing any problems or you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us in the comments section below, and we’ll get back to your ASAP.
All right, time to take your first step into the world of SEO!


